What Tests & Cancer Treatments for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Are Available in Canada?
Table of Contents
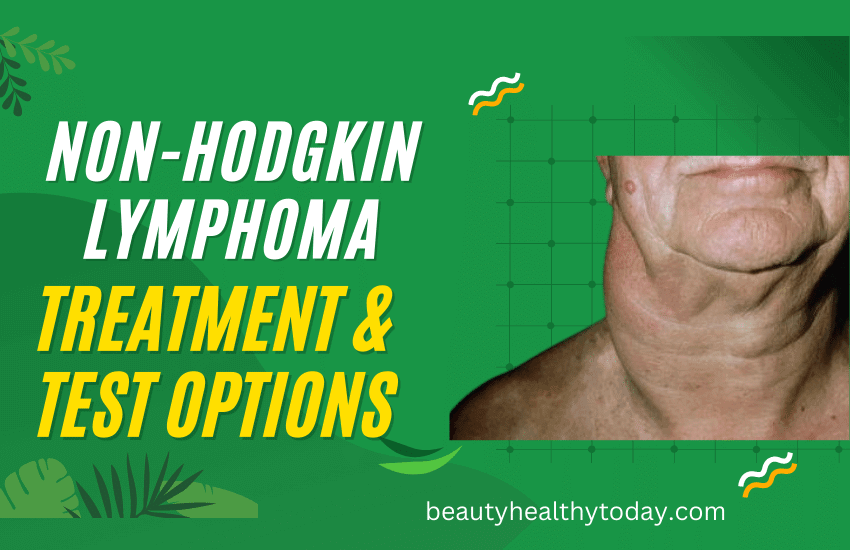
There are a variety of cancer treatments available in Canada for those suffering from non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). This cancer begins in your lymphatic system, which is a part of your body’s immune system which fights germs and viruses. In non-Hodgkin lymphoma, white blood cells (known as lymphocytes) grow abnormally and may form tumours or growths throughout your body.
There are different treatments, and the kind you need will depend on several personal factors, such as the stage of cancer and your age.
Let’s discuss these treatments and the tests that are done to detect them.
Types of Tests & Cancer Treatments for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Canada
Here are a few tests that are done to diagnose NHL and the treatments available in Canada.
Blood Tests
These tests help your healthcare provider get a view of your overall health. They may test your blood for viruses related to non-Hodgkin lymphoma or symptoms of this lymphoma.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
This blood test counts your blood cells.
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Levels
This test is done to measure LDH levels. High LDH levels may indicate lymphoma, tissue damage, or other ailments such as liver and kidney disease.
Blood Chemistry Study
This test counts the substances that your tissues or organs release into the bloodstream.
Imaging Tests
These tests help your healthcare providers know about the changes occurring in your body, like lumps or tumours.
Ultrasounds
In this procedure, ultrasound or high-energy sound waves bounce off the internal organs and tissues and make echoes. These echoes then create a sonogram which is an image of the body’s tissues.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans
This procedure uses a small amount of radioactive tracer to identify malignant tissues.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scans
This uses radio waves, a magnet, and a computer to make multiple detailed images of the areas inside the body.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scans
This scanning creates several detailed pictures of the areas inside the body.
Other Tests
Hepatitis C & B: Healthcare providers test for hepatitis C and B markers in order to help plan out treatment for non-Hodgkin lymphoma. These markers are antibodies and virus-specific antigens. Diverse markers emphasize if you have ever been exposed to these harmful viruses.
Biopsy: In this procedure, a surgeon removes the lymph node. If they remove the whole lymph node, it is known as an excisional biopsy. If only a small portion of a bigger node or tumour is taken away, it is referred to as an incisional biopsy.
Immunophenotyping: This procedure helps to diagnose specific types of lymphoma such as Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It uses antibodies to detect malignant cells based on the kinds of markers or antigens present on the cells’ surface. (The human body makes antibodies in order to fight foreign substances. Antigens are the substances that can activate your immune system.)
Cancer Treatments for NHL Patients in Canada
Here are the cancer treatments available for patients suffering from non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Active Surveillance
If you have a slow-growing form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, such as follicular lymphoma, but have no symptoms, your healthcare providers delay treatments or medications. This is called active surveillance or watchful waiting. They keep an eye on your health so they may start the treatment the moment you show symptoms.
Chemotherapy
This widely-used treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma uses drugs to kill malignant cells. Generally, you will get chemotherapy via drip directly into a vein, via tablets taken by mouth, or a combination of the two. The side effects of chemotherapy include a reduction in normal blood cells, loss of hair, and nausea.
High-Dose Chemotherapy
If your lymphoma is not getting better with initial chemotherapy, then you will need a stronger dose. This rigorous chemotherapy may damage bone marrow. If so then you may have to undergo a stem cell or bone marrow transplant to replace affected blood cells with healthy ones. (Bone marrow is a spongy tissue found in the centre of some bones such as hip or thigh bones. Stem cells are special cells or raw materials from which different cells with specialized functions are produced.)
Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
Often for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, your healthcare provider may use a type of medicine known as a monoclonal antibody. These medicines attach themselves to malignant and healthy cells and then signal your immune system to attack or kill the cells. Once the treatment is over, the level of healthy cells goes back to normal in due course. Monoclonal antibody therapy may be your sole treatment, or often they are prescribed along with chemotherapy to make the cancer treatment more effective.
Radiationw Therapy
This is most often used to treat NHL in the early stages, where it is still restricted to one area of the body. The duration of the whole treatment will depend on your age and what stage it is at, among other factors. The side effects of radiotherapy are dry mouth, appetite loss, nausea, fatigue, red skin, or soreness in the area of treatment.
Steroids
This is commonly used in combination with chemotherapy for non-Hodgkin lymphoma treatment in order to make chemotherapy more successful. The medicine is usually given as injections or tablets in conjunction with your chemotherapy.
Undoubtedly, cancer treatments and tests for non-Hodgkin lymphoma in Canada are quite difficult to deal with. However, with the help of caregivers, healthcare professionals and support groups, your chances of recovery are high. Today, many patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma get cured and can lead a normal life for a long time.